Endoplasmic Reticulum Drawing Cytoplasm Cartoons, Illustrations & Vector Stock Images Leadrisers
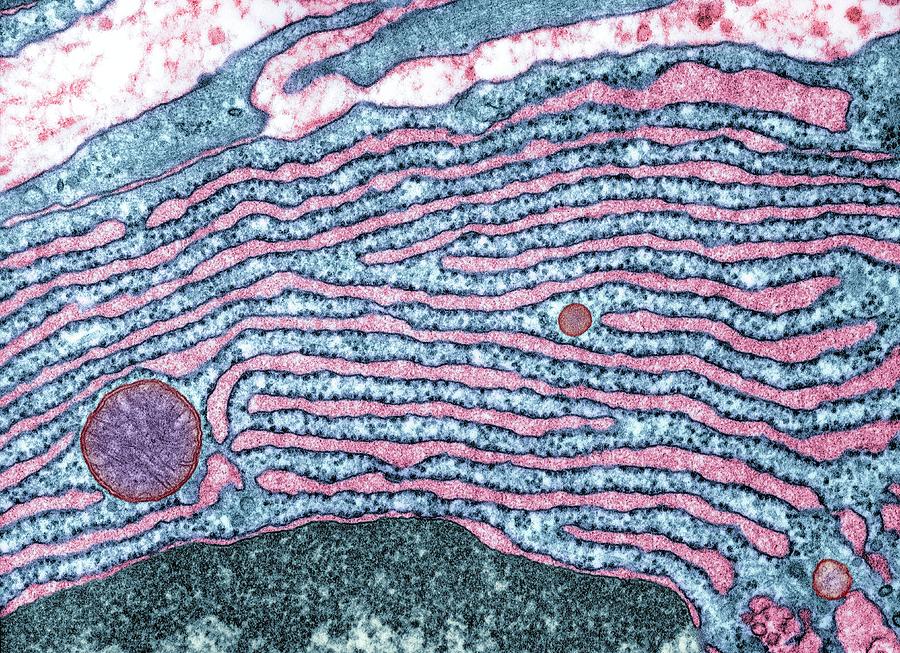
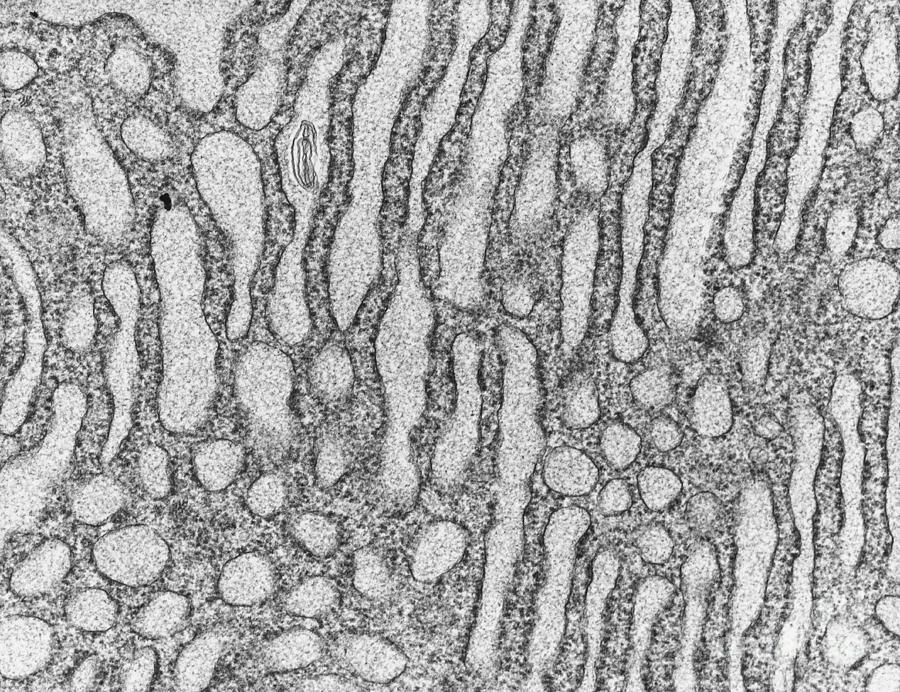
Figure 5.9.2 5.9. 2: (a) The ER is a winding network of thin membranous sacs found in close association with the cell nucleus. The smooth and rough endoplasmic reticula are very different in appearance and function (source: mouse tissue). (b) Rough ER is studded with numerous ribosomes, which are sites of protein synthesis (source: mouse tissue).

What Is The Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum Like In Real Life
At a Glance Advanced imaging techniques revealed a more accurate picture of how the peripheral endoplasmic reticulum is structured. The findings may yield new insights for genetic diseases affecting proteins that help shape the endoplasmic reticulum.
Endoplasmic Reticulum Photograph by Steve Gschmeissner Pixels
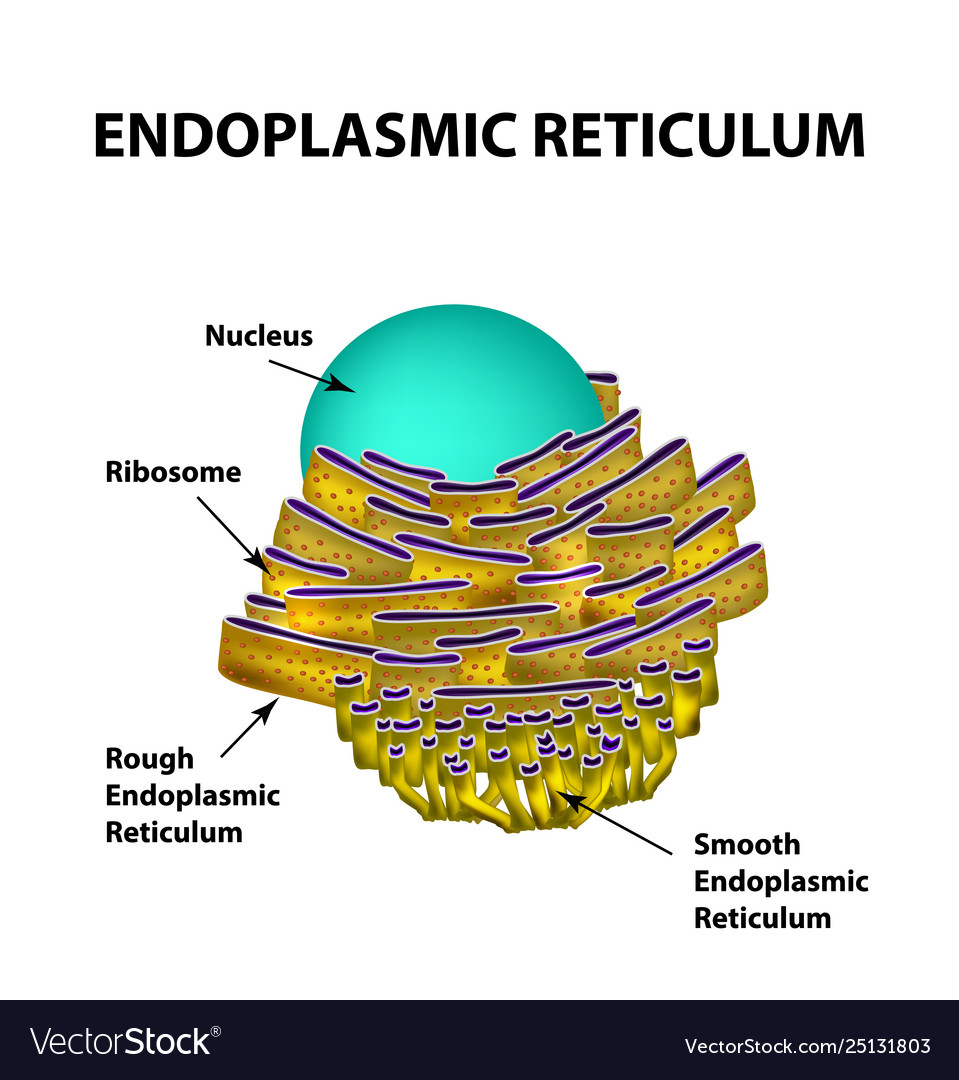
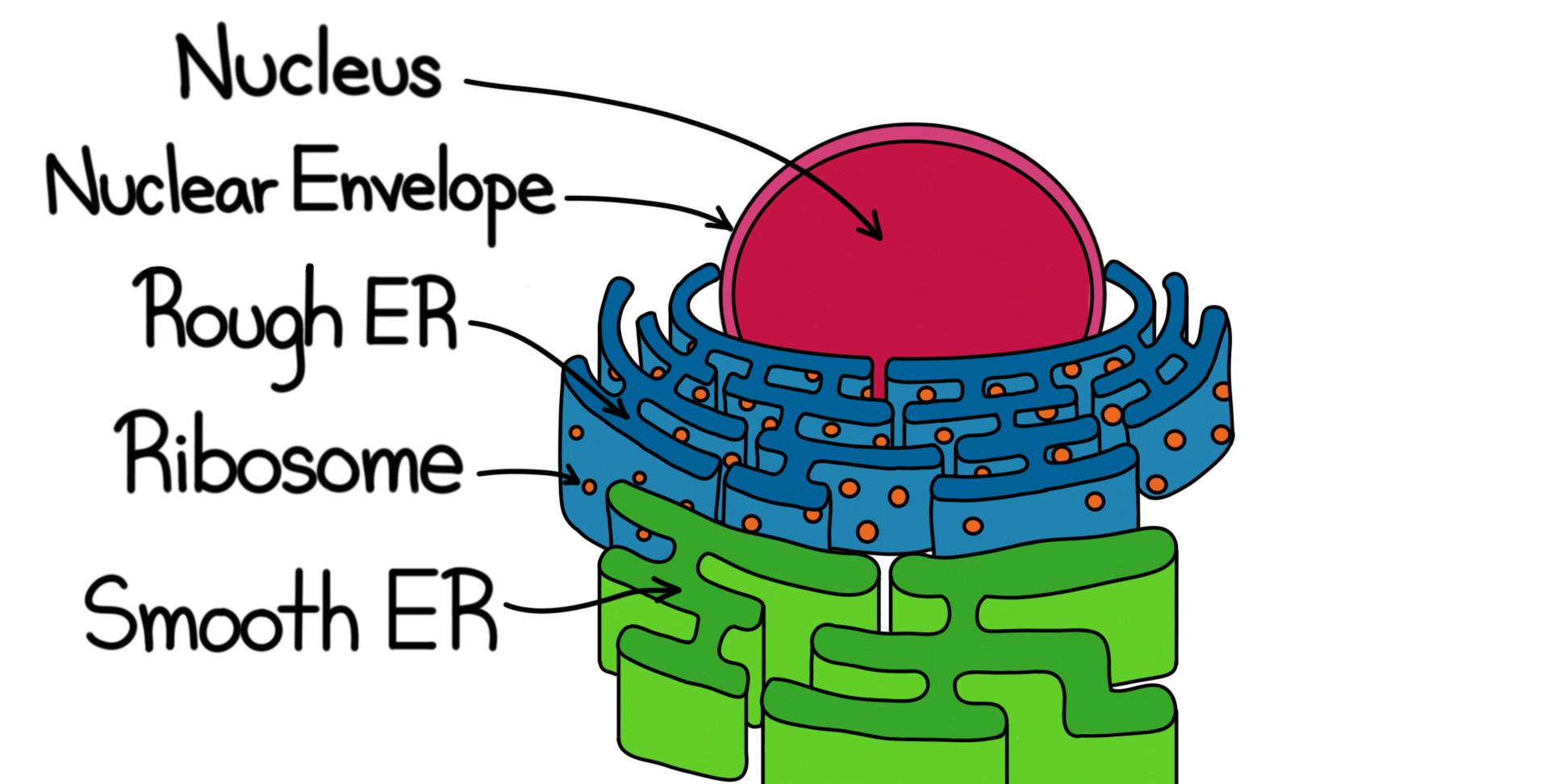
The endoplasmic reticulum is a type of organelle found in eukaryotic cells that forms an interconnected network of flattened, membrane-enclosed sacs or tube-like structures known Education Chart of Biology for Endoplasmic Reticulum Diagram. Vector illustration. The structure of Animal cell
Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum Photograph by Medimage/science Photo Library Fine Art America
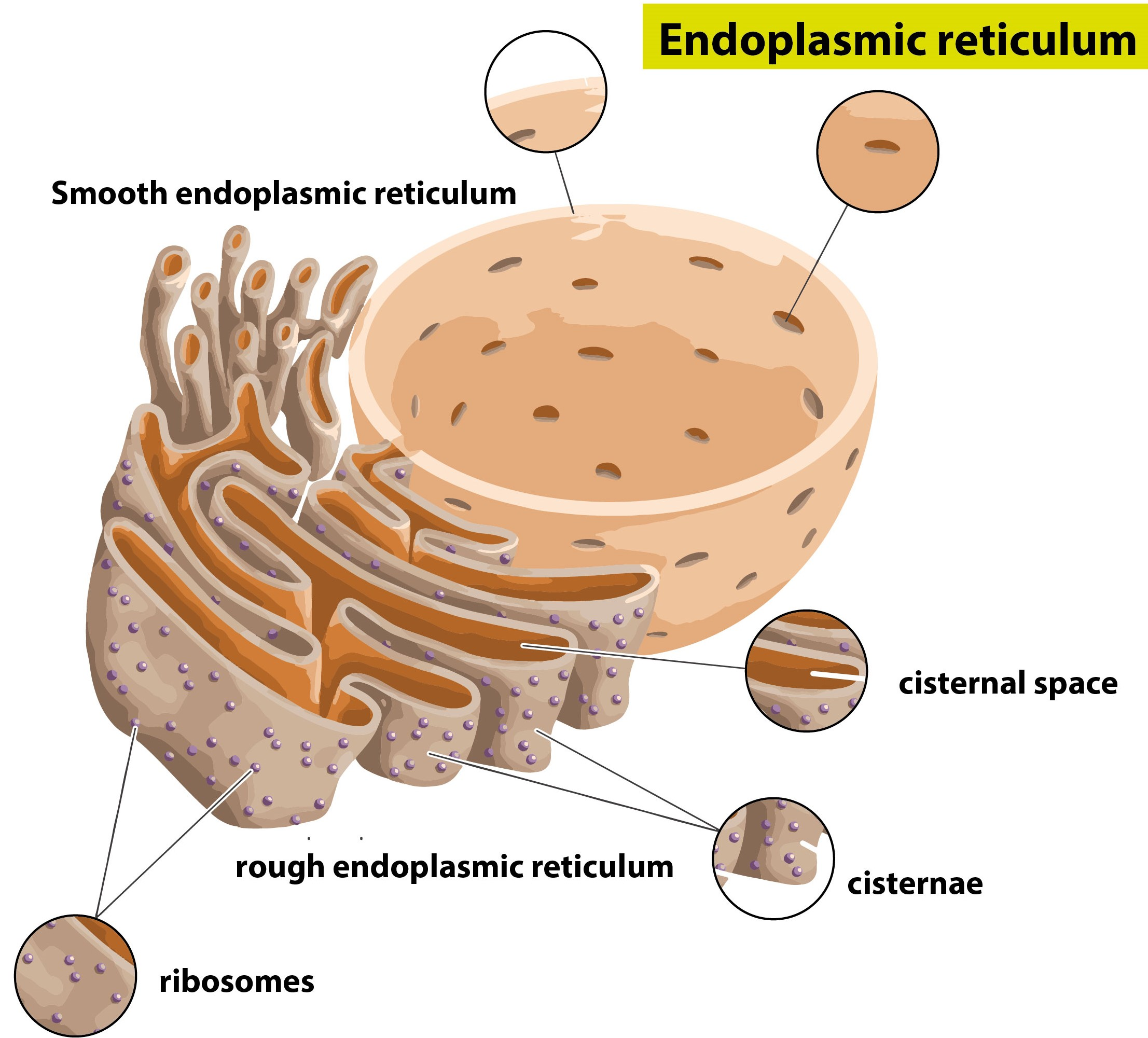
The endoplasmic reticulum ( ER) is, in essence, the transportation system of the eukaryotic cell, and has many other important functions such as protein folding. It is a type of organelle made up of two subunits - rough endoplasmic reticulum ( RER ), and smooth endoplasmic reticulum ( SER ).

Endoplasmic reticulum structure infographics Vector Image
The endoplasmic reticulum is a network of sacs that manufactures, processes, and transports chemical compounds for use inside and outside of the cell.. Presented in Figure 2 is a fluorescence digital image taken through the microscope of the endoplasmic reticulum network in a bovine (cow) pulmonary artery endothelial cell grown in culture.
Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum (RER) — Structure & Function Expii
The endoplasmic reticulum is a network of tubules and flattened sacs that serve a variety of functions in plant and animal cells . The two regions of the ER differ in both structure and function. Rough ER has ribosomes attached to the cytoplasmic side of the membrane. Smooth ER lacks attached ribosomes.
The surface of the endoplasmic reticulum is covered by (a) Glucose(b) DNA(c) Ribosomes(d) RNA
endoplasmic reticulum (ER), in biology, a continuous membrane system that forms a series of flattened sacs within the cytoplasm of eukaryotic cells and serves multiple functions, being important particularly in the synthesis, folding, modification, and transport of proteins . All eukaryotic cells contain an endoplasmic reticulum (ER).
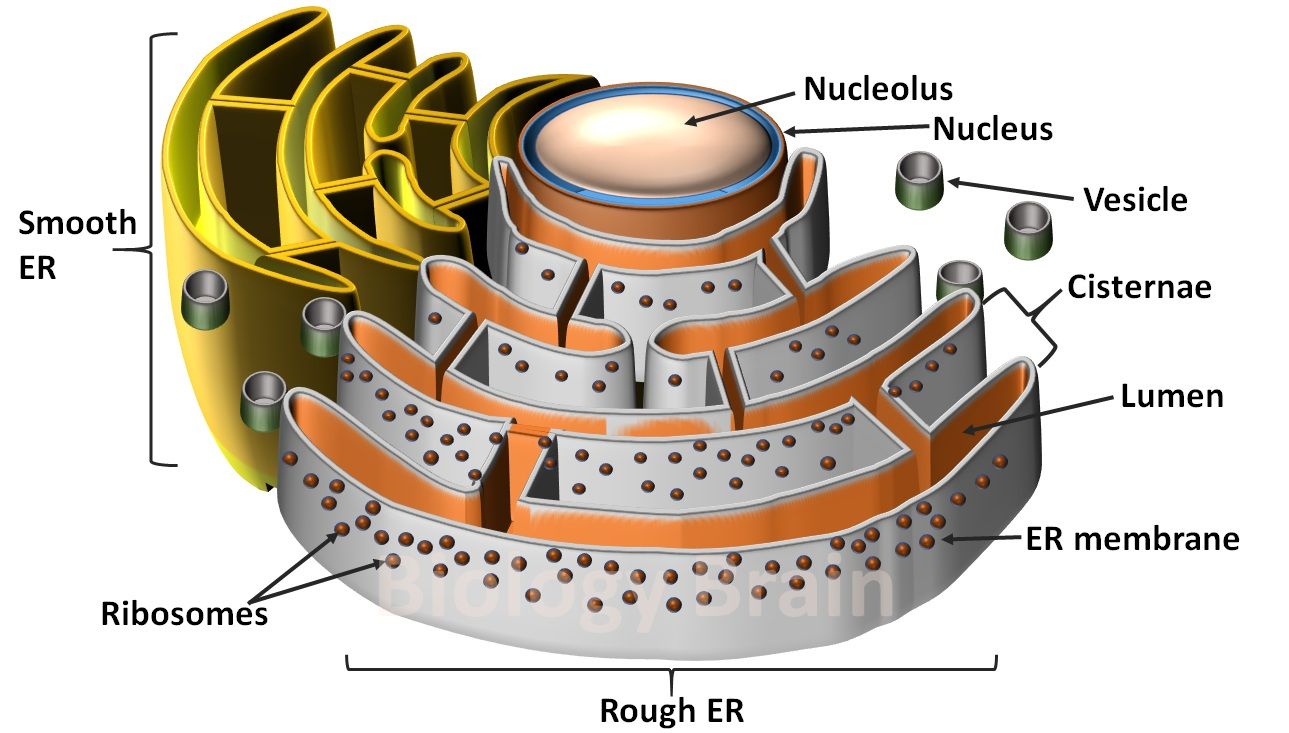
Diagram of Endoplasmic Reticulum Definition, Types, Function and Structure Biology Brain
mitochondria. ribosome. lysosome. golgi apparatus. nucleus. of 9. NEXT. Browse Getty Images' premium collection of high-quality, authentic Endoplasmic Reticulum stock photos, royalty-free images, and pictures. Endoplasmic Reticulum stock photos are available in a variety of sizes and formats to fit your needs.
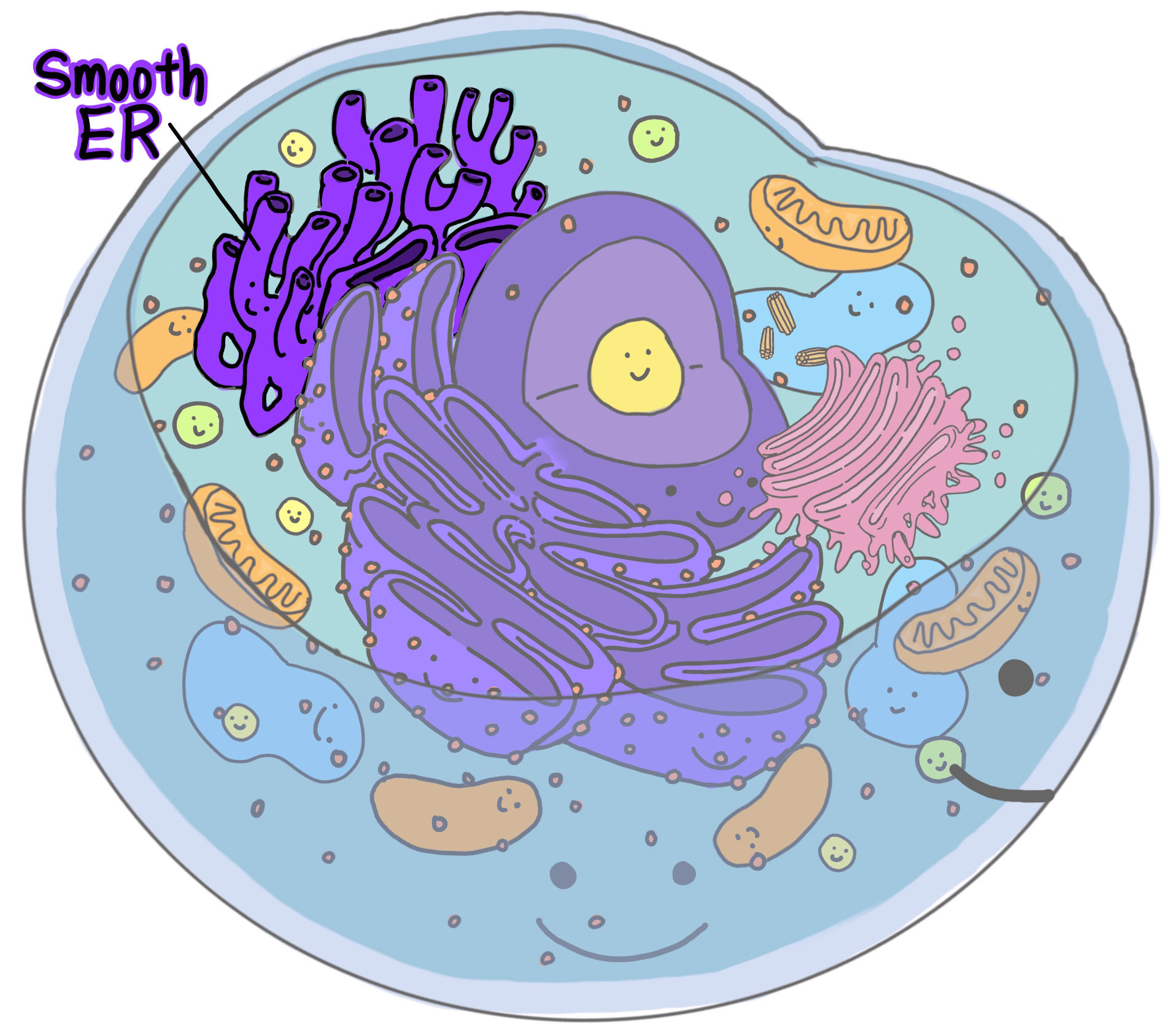
Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum (SER) — Structure & Function Expii
The endoplasmic reticulum (ER) is a large, dynamic structure that serves many roles in the cell including calcium storage, protein synthesis and lipid metabolism.. b ER morphology from the same HeLa cell depicting an image plane closer to the coverslip. This highlights the complexity of the peripheral ER. c ER network formed in Xenopus egg.

The Endoplasmic Reticulum, Epilepsy, & Cell Stress Science Over a Cuppa
The Endoplasmic Reticulum All eucaryotic cells have an endoplasmic reticulum ( ER). Its membrane typically constitutes more than half of the total membrane of an average animal cell (see Table 12-2 ). The ER is organized into a netlike labyrinth of branching tubules and flattened sacs extending throughout the cytosol ( Figure 12-35 ).
/endoplasmic_reticulum-56cb365f3df78cfb379b574e.jpg)
The Structure and Function of the Endoplasmic Reticulum
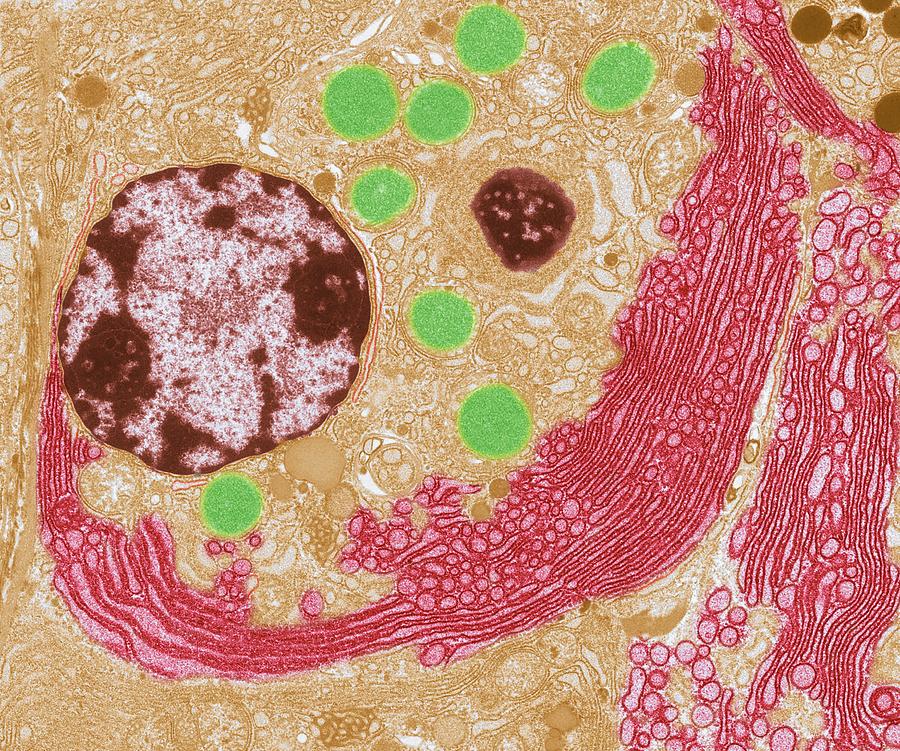
This microscopic image shows the nucleus surrounded by the endoplasmic reticulum. The folds in the structure promote the surface area. The presence of ER in cells depends on the function of the cell.
Endoplasmic Reticulum Tem Photograph by David M. Phillips Pixels
This is a microscopic image of a section from mammalian lung tissue. The bottom right corner of the image shows the nucleus and the rest of the picture illustrates the extensive nature of the ER. Small dark circles are mitochondria that exist in physical proximity with the membranes of the ER. Endoplasmic Reticulum Function

Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum, TEM Stock Image C040/3844 Science Photo Library
The endoplasmic reticulum (ER) is a heterogeneous organelle with distinct morphologies of sheets and an interconnected network of tubules sharing a common lumen. An ER domain marked by the Rab10.
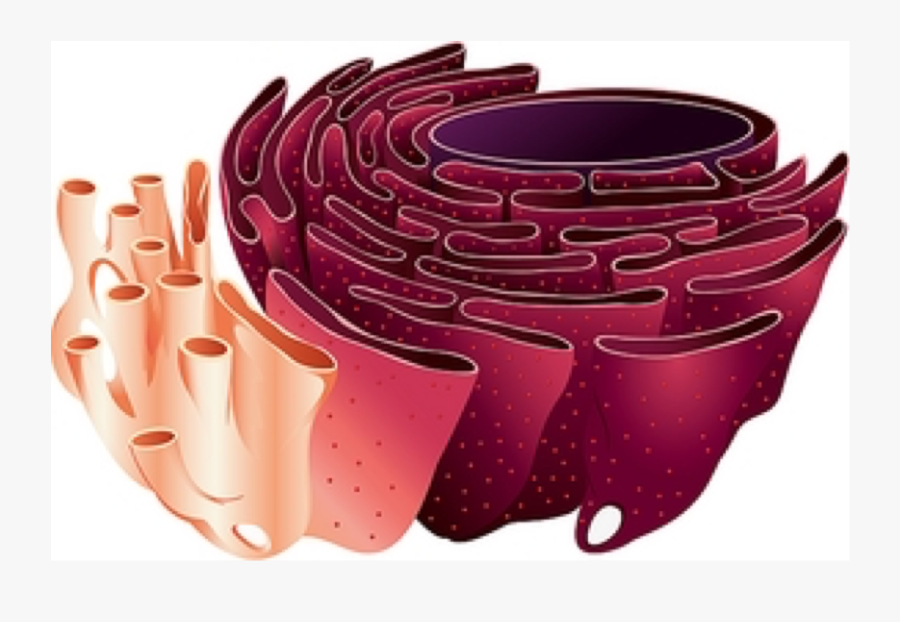
An Animal Cell Endoplasmic Reticulum The Morphology and Function of Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER
Browse 1,000+ endoplasmic reticulum stock photos and images available, or search for mitochondria or ribosome to find more great stock photos and pictures. mitochondria ribosome lysosome golgi apparatus nucleus rough endoplasmic reticulum golgi chloroplast smooth endoplasmic reticulum vacuole Sort by: Most popular

Endoplasmic Reticulum ( Read ) Biology CK12 Foundation
The endoplasmic reticulum ( ER) plays a key role in the modification of proteins and the synthesis of lipids. It consists of a network of membranous tubules and flattened sacs. The discs and tubules of the ER are hollow, and the space inside is called the lumen. Rough ER

Endoplasmic Reticulum The Lipid and Protein Processing Machinery of the Cell I Fly Bio
The Endoplasmic Reticulum. The endoplasmic reticulum (ER) is a series of interconnected membranous sacs and tubules that collectively modifies proteins and synthesizes lipids. However, these two functions are performed in separate areas of the ER: the rough ER and the smooth ER. The hollow portion of the ER tubules is called the lumen or.